General (GT) Test 1 – Passage 05: Paper Recycling reading answers with location, explanation and pdf summary. This reading paragraph has been taken from our huge collection of Academic & General Training (GT) Reading practice test PDF’s.

IELTS reading module focuses on evaluating a candidate’s comprehension skills and ability to understand English. This is done by testing the reading proficiency through questions based on different structures and paragraphs (500-950 words each). There are 40 questions in total and hence it becomes extremely important to practice each and every question structure before actually sitting for the exam.
This reading passage mainly consists of following types of questions:
- Summary completion
- Flow-chart completion
We are going to read about how the recycling of paper is done. You must read the passage carefully and try to answer all questions correctly.
Reading Passage 05
Paper Recycling
A. Paper is different from other waste produce because it comes from a sustainable resource: trees. Unlike the minerals and oil used to make plastics and metals, trees are replaceable. Paper is also biodegradable, so it does not pose as much threat to the environment when it is discarded. While 45 out of every 100 tonnes of wood fibre used to make paper in Australia comes from waste paper, the rest comes directly from virgin fibre from forests and plantations. By world standards this is a good performance since the world-wide average is 33 per cent waste paper. Governments have encouraged waste paper collection and sorting schemes and at the same time, the paper industry has responded by developing new recycling technologies that have paved the way for even greater utilisation of used fibre. As a result, industry’s use of recycled fibres is expected to increase at twice the rate of virgin fibre over the coming years.
B. Already, waste paper constitutes 70% of paper used for packaging and advances in the technology required to remove ink from the paper have allowed a higher recycled content in newsprint and writing paper. To achieve the benefits of recycling, the community must also contribute. We need to accept a change in the quality of paper products; for example stationery may be less white and of a rougher texture. There also needs to be support from the community for waste paper collection programs. Not only do we need to make the paper available to collectors but it also needs to be separated into different types and sorted from contaminants such as staples, paperclips, string and other miscellaneous items.
C. There are technical limitations to the amount of paper which can be recycled and some paper products cannot be collected for re-use. These include paper in the form of books and permanent records, photographic paper and paper which is badly contaminated. The four most common sources of paper for recycling are factories and retail stores which gather large amounts of packaging material in which goods are delivered, also offices which have unwanted business documents and computer output, paper converters and printers and lastly households which discard newspapers and packaging material. The paper manufacturer pays a price for the paper and may also incur the collection cost.
D. Once collected, the paper has to be sorted by hand by people trained to recognise various types of paper. This is necessary because some types of paper can only be made from particular kinds of recycled fibre. The sorted paper then has to be repulped or mixed with water and broken down into its individual fibres. This mixture is called stock and may contain a wide variety of contaminating materials, particularly if it is made from mixed waste paper which has had little sorting. Various machinery is used to remove other materials from the stock. After passing through the repulping process, the fibres from printed waste paper are grey in colour because the printing ink has soaked into the individual fibres. This recycled material can only be used in products where the grey colour does not matter, such as cardboard boxes but if the grey colour is not acceptable, the fibres must be de-inked. This involves adding chemicals such as caustic soda or other alkalis, soaps and detergents, water-hardening agents such as calcium chloride, frothing agents and bleaching agents. Before the recycled fibres can be made into paper they must be refined or treated in such a way that they bond together.
E. Most paper products must contain some virgin fibre as well as recycled fibres and unlike glass, paper cannot be recycled indefinitely. Most paper is down-cycled which means that a product made from recycled paper is of an inferior quality to the original paper. Recycling paper is beneficial in that it saves some of the energy, labour and capital that goes into producing virgin pulp. However, recycling requires the use of fossil fuel, a non-renewable energy source, to collect the waste paper from the community and to process it to produce new paper. And the recycling process still creates emissions which require treatment before they can be disposed of safely. Nevertheless, paper recycling is an important economical and environmental practice but one which must be carried out in a rational and viable manner for it to be useful to both industry and the community.
Questions 30-36
Complete the summary below of the first two paragraphs of the Reading Passage. Choose ONE OR TWO WORDS from the Reading Passage for each answer. Write your answers in boxes 30-36 on your answer sheet.
| SUMMARY Firstly it comes from a resource which is … (30) … and secondly it is less threatening to our environment when we throw it away because it is … (31) … Although Australia’s record in the re-use of waste paper is good, it is still necessary to use a combination of recycled fibre and … (32) .. to make new paper. The paper industry has contributed positively and people have also been encouraged by … (33) … to collect their waste on a regular basis. One major difficulty is the removal of ink from used paper but … (34) … are being made in this area. However, we need to learn to accept paper which is generally of a lower … (35) … than before and to sort our waste paper by removing .. (36) .. before discarding it for collection. |
Questions 37-41
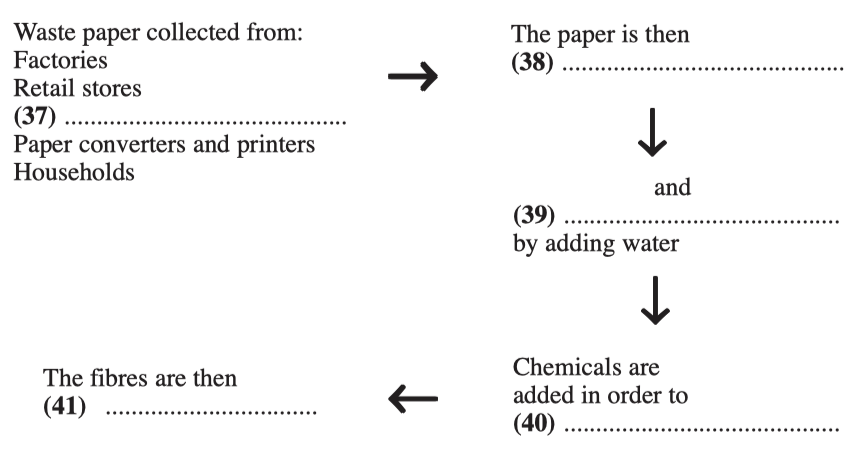
Look at paragraphs C, D, and E and, using the information in the passage, complete the flow chart below. Write your answers in boxes 37-41 on your answer sheet.
Use ONE OR TWO WORDS for each answer.
Answers with Explanation
Check out your Paper Recycling reading answers below with locations and explanations given in the text.
| Questions/ Task/ Skills tested | ||
| 30-36 | Summary completion | • skimming for information • understanding paraphrase • rewording text |
| 37-41 | Flow chart completion | • skimming for specific information • following a process • summarising ideas |
Questions 30-36
(Suggested approach)
• Read the task rubric carefully.. You have to complete the summary by filling in the spaces with words from the passage. The words must fit in meaning and also be grammatically correct.
• Read the summary to familiarise yourself with it. It may be possible to find words without reading the original text, but if you do this you may pick words which are not in the text, in which case your answer will be incorrect. So you must look for a word within the passage which has the right meaning and which is the correct part of speech for the space.
• Read the first item in the summary.
• Look at the text and see if you can find the same information there. For item 30, the first sentence discusses the qualities of paper that make it different from other waste products. The text states that paper comes from a “sustamable resource”. So “sustamable” is a correct answer.
• Sometimes there are alternative answers that are correct in this type of question. For item 30, “replaceable” is also a possible answer because it says a little further on in the text, “trees are replaceable”.
• Note however that “renewable” is not an acceptable answer because although it is a synonym and makes sense, it is not in the original text.
| Question | Answer/ Location of answer in text | |
| 30 | sustamable// replaceable | “Paper … comes from a sustamable resource …” |
| 31 | biodegradable | “Paper is also biodegradable, so it does not pose as much threat to the environment when it is discarded.” |
| 32 | virgin fibre/ pulp | “… the rest comes directly from virgin fibre …” |
| 33 | governments //the government | “Governments have encouraged waste paper collection and sorting schemes …” |
| 34 | advances | “… advances in the technology required to remove ink …” |
| 35 | quality | “We need to accept a change in the quality of paper products” |
| 36 | contaminants | “… it also needs to be sorted from contaminants |
| Question | Answer |
| 37 | offices |
| 38 | sorted |
| 39 | (re)pulped |
| 40 | de-ink/remove ink//make white |
| 41 | refined |
Have any doubts??? Discuss in the comments ...
If you want the Paper Recycling reading pdf, please write your email in the comment section below. We’ll send it across at the speed of light.
or
You can buy the complete booklet here at discounted price.
All the best !
| Disclosure: We sometimes use affiliate links in our content. This means if you click on the link and purchase an item, we’ll receive an affiliate commission at no extra cost to you. These links help us to offset the costs of running this website. Thanks for understanding! |
Plz help me ielts modules
Sure!
Please, send me all IELTS GT reading (all reading passages)
Dear Sir,
I need urgently general reading book in pdf for my IELTS exam in december-2022.